【摘要】 青岛科技大学袁勋团队在《Advanced Materials》发表研究,开发亚纳米铁团簇电极材料,实现法拉第电容去离子技术性能突破。科学指南针提供吸附能和内应力计算支持,助力机理解析。
青岛科技大学袁勋教授团队在《Advanced Materials》发表创新研究成果,通过孔介导气相扩散策略成功合成亚纳米铁团簇(0.8 nm),并应用于法拉第电容去离子技术,实现高效海水淡化。科学指南针为本研究提供吸附能和内应力计算支持,助力材料设计与机理解析。
研究背景与海水淡化挑战
高熔点非贵金属超小纳米团簇合成策略缺失制约高效海水淡化技术发展。法拉第电容去离子技术面临动力学缓慢和循环稳定性差的双重瓶颈,亟需创新材料解决方案。
核心技术瓶颈:
-
高熔点金属如Fe、Ti、Mn等超小纳米团簇合成困难
-
传统方法无法实现亚纳米尺度精确控制
-
电容去离子技术离子扩散动力学缓慢
-
循环过程中应力积累导致材料结构失效
-
氯离子存储机制不明确,制约理性设计
创新方法:孔介导气相扩散策略
研究团队开发孔介导气相扩散新方法,实现亚纳米铁团簇的可控合成,为高效海水淡化电极材料设计提供新途径。
技术突破要点:
-
采用Fe(acac)₃为前驱体,通过精确温度控制实现气相扩散
-
利用中空碳球介孔通道作为空间限制模板
-
两步法调控:160°C促进升华,240°C实现热分解
-
实现0.8 nm铁团簇均匀分布,尺寸分布狭窄
-
方法可扩展至Ti、Co、Mn等其他高熔点金属
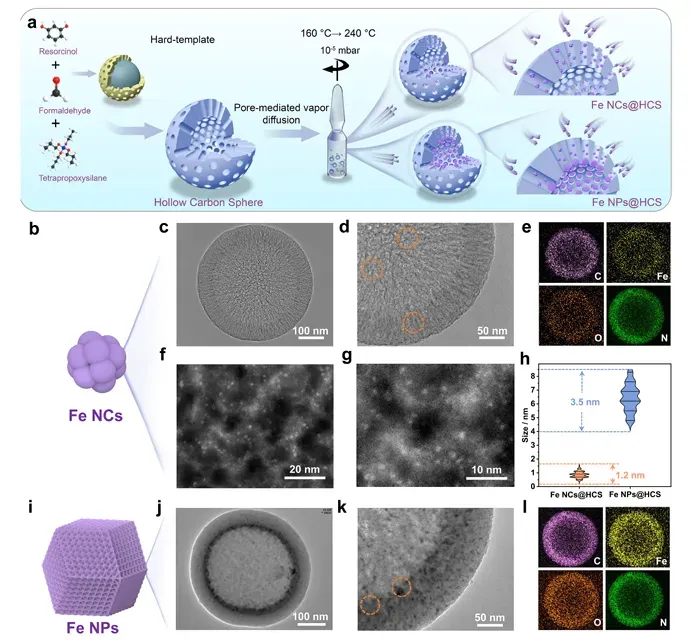
Figure 1
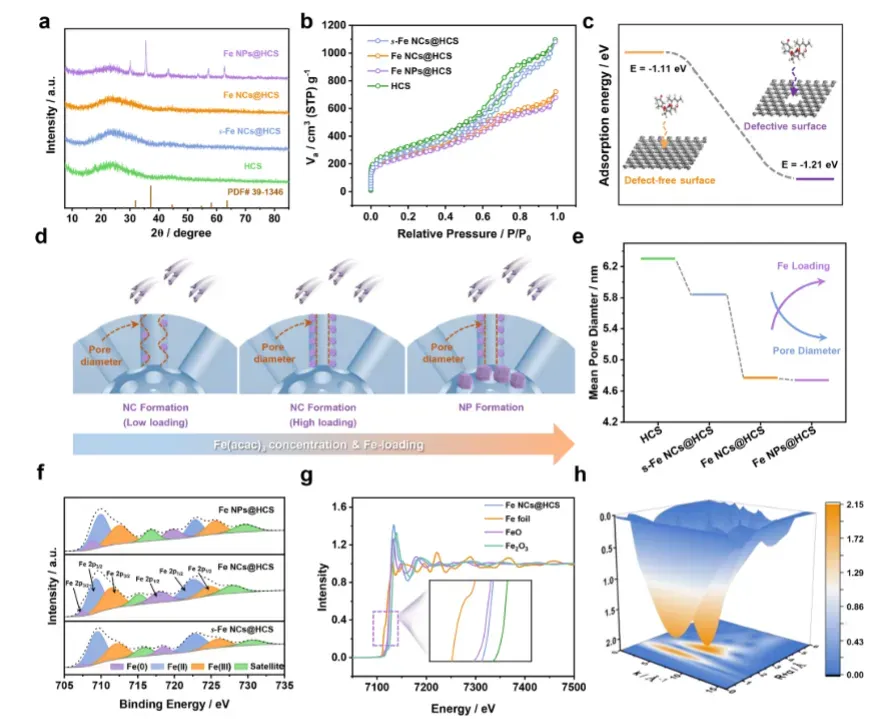
材料合成与结构表征
通过系统表征证实亚纳米铁团簇成功合成并均匀分布,展现精确的结构控制能力。
结构特征验证:
-
TEM和HAADF-STEM显示0.8 nm铁团簇均匀分布
-
XRD证实非晶结构,无明显结晶峰
-
BET显示高比表面积(944.17 m² g⁻¹),介孔结构保留
-
TGA定量铁负载量(8.52%)
-
XPS证实Fe(0)、Fe(II)、Fe(III)共存状态
合成机制解析:
-
前驱体负载量调控团簇尺寸与分布
-
缺陷碳位点优先吸附,结合能-1.21 eV
-
孔径变化证实团簇在孔道内形成
-
过量前驱体导致大颗粒生成
Figure 2
理论计算与吸附机制
科学指南针支持的密度泛函理论计算深入揭示前驱体吸附机制和尺寸效应,为合成优化提供理论指导。
计算研究发现:
-
吸附能计算显示缺陷位点结合能(-1.21 eV)优于原始位点(-1.11 eV)
-
内应力模拟证实亚纳米尺寸有效降低应力积累
-
电解质渗透速率分析揭示尺寸依赖的扩散行为
-
Cl⁻浓度分布模拟验证团簇尺寸效应
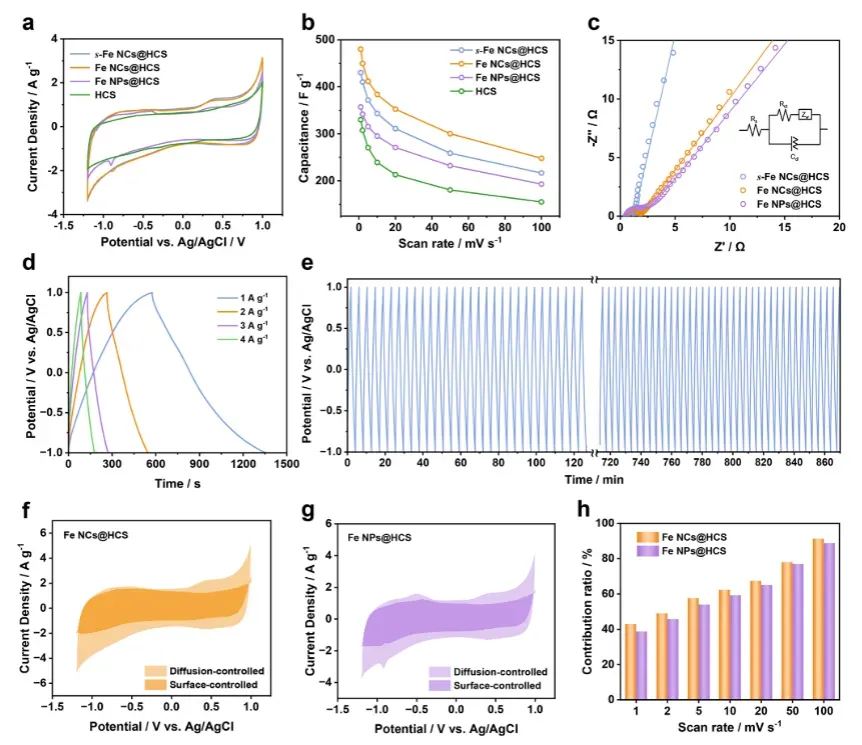
Figure 3
电化学性能评估
亚纳米铁团簇电极展现卓越的电化学性能,突破传统电容去离子技术限制。
性能卓越表现:
-
比电容达480 F g⁻¹,显著优于对比样品
-
电荷转移阻抗低至1.18 Ω,动力学优异
-
200次循环后容量保持率86.47%
-
表面控制贡献占比62.4%,促进快速响应
-
恒流充放电曲线对称,可逆性良好
尺寸效应关键作用:
-
亚纳米尺寸提供高比表面积和活性位点
-
增强电极-电解质界面相互作用
-
促进离子快速扩散和电荷转移
-
有效缓解循环过程中的应力积累
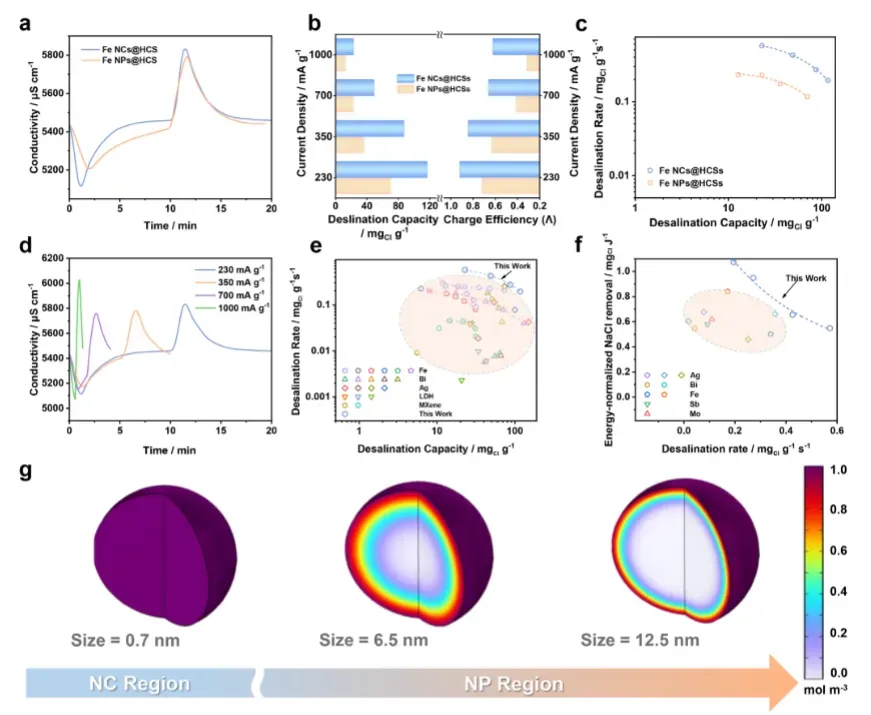
Figure 4
海水淡化性能与应用
在实际海水淡化测试中,亚纳米铁团簇电极展现出突破性性能,验证其应用潜力。
淡化性能突破:
-
盐吸附量高达116.83 mg Cl g⁻¹
-
脱盐速率0.57 mg Cl g⁻¹ s⁻¹
-
200次循环后容量保持86.47%
-
能耗归一化NaCl去除量显著优于对比材料
-
实际海水测试中性能稳定,适应性强
现场验证结果:
-
总电极面积0.25 m²体系成功应用
-
电导率、总有机碳、菌体浓度显著降低
-
不同盐度条件下性能稳定
-
展示实际应用可行性
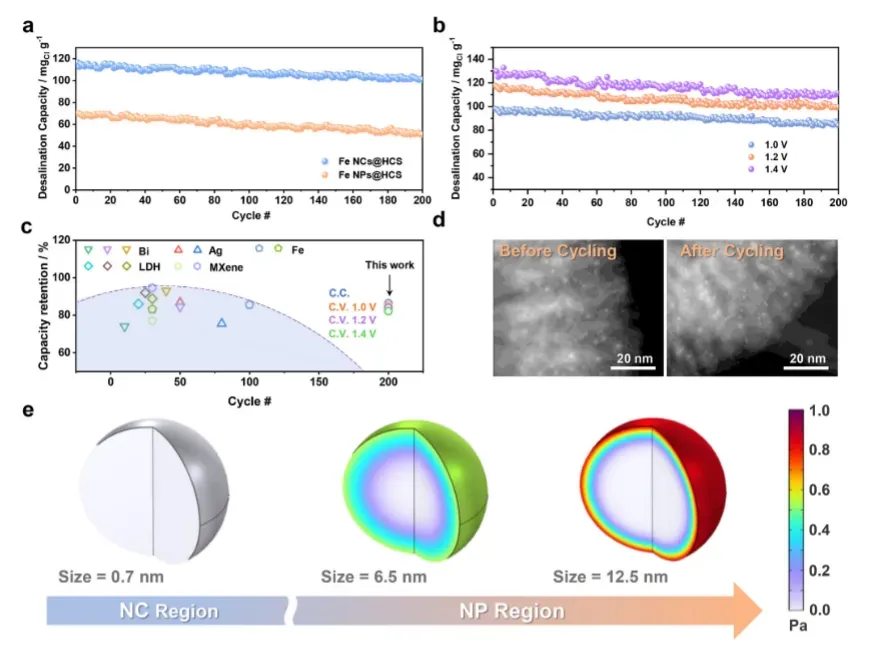
Figure 5
机理研究与存储机制
通过同步辐射和理论计算明确氯离子存储机制,解决长期存在的机理争议。
机制解析突破:
-
操作X射线吸收光谱证实Fe→FeOCl转化路径
-
EXAFS显示Fe-O配位数增加,Fe-Fe配位数减少
-
DFT计算验证FeOCl形成能垒(1.41 eV)低于FeCl₃(1.46 eV)
-
氯离子存储通过转化反应进行,非插层机制
科学指南针计算贡献:
-
吸附能计算指导合成策略优化
-
内应力模拟揭示尺寸效应机制
-
反应路径计算验证存储机理
-
为实验设计提供理论支撑
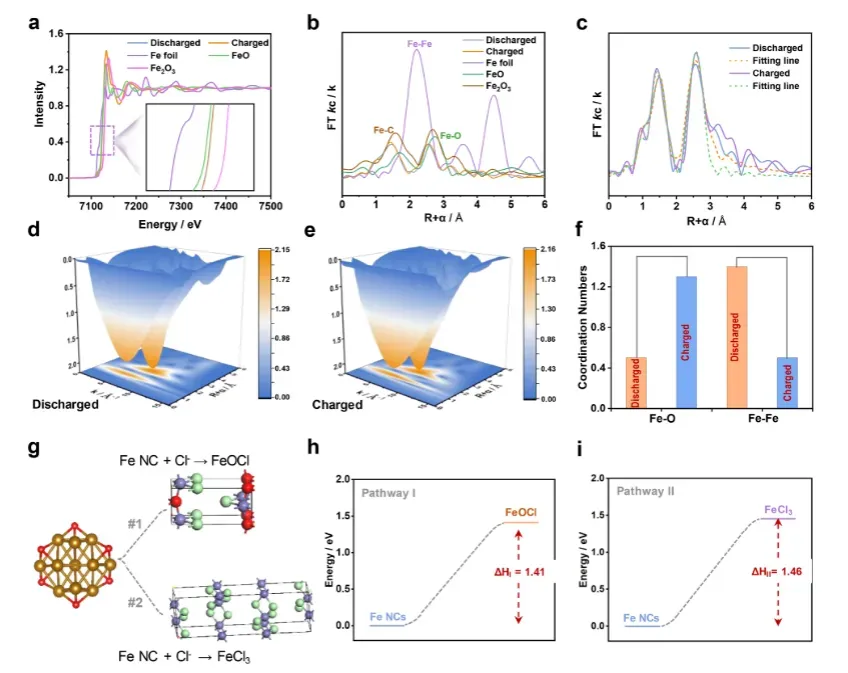
Figure 6
总结与展望
亚纳米铁团簇材料为高效海水淡化提供创新解决方案,推动电容去离子技术发展。
创新价值总结:
-
孔介导气相扩散实现亚纳米团簇可控合成
-
亚纳米尺寸效应解决动力学和稳定性瓶颈
-
明确氯离子存储机制,指导理性材料设计
-
科学指南针计算支持为机理解析提供关键支撑
应用前景:
-
高效节能海水淡化系统
-
工业废水处理与资源回收
-
便携式淡水制备装置
-
可持续水处理技术开发
论文信息:Advanced Materials, 2025
DOI:10.1002/adma.202517511
科学指南针计算服务:提供吸附能、内应力计算支持,助力材料设计与性能优化。了解更多:https://www.shiyanjia.com/simulate.html【科学指南针·服务声明·2025】









 您已经拒绝加入团体
您已经拒绝加入团体

 2025-12-23
2025-12-23
 595
595
 0
0