【摘要】 作为最实用的储能系统,碱金属离子电池因具有长寿命和高功率密度等特点引起了广泛的关注。其中,金属硫化物例如MoS2具有显著的容量和丰富的氧化还原电位,被广泛应用于储能领域,然而它们的离子存储能力仍受限于多硫化物的溶解和缓滞的电化学动力学。

文 章 信 息
研 究 背 景
文 章 简 介
本 文 解 析
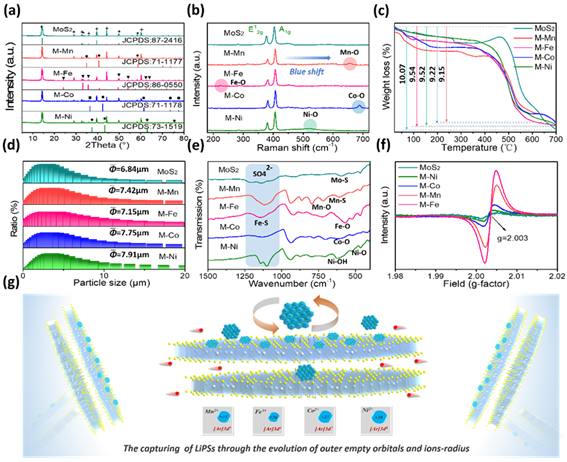
图1 纯MoS2和MoS2@MOx 复合材料的物化性质及储锂机制示意图
Figure. 1 The physical-chemical properties of the as-obtained samples: XRD patterns (a), Raman spectrums (b), TG curves (c), particle size distribution (d), FT-IR spectrums (e), ESR spectrums (f), and the simplified lithium storage mechanism of MoS2@MOx (g).
要点二:Mo-S-M型界面化学键的构筑
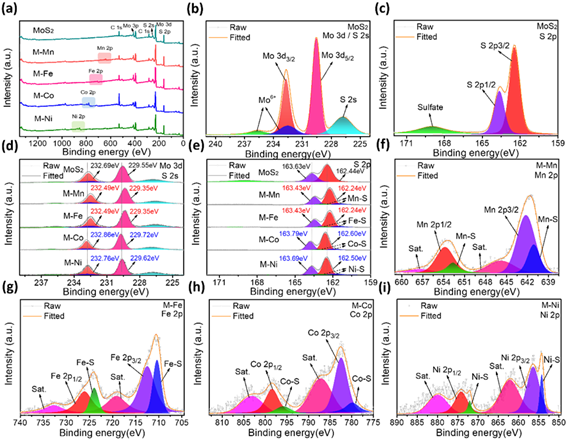
图2 纯MoS2和MoS2@MOx 复合材料的XPS图谱分析
Figure. 2 XPS spectra of the as-obtained samples: survey XPS spectrums (a), high-resolution spectrums Mo 3d and S 2p of MoS2 (b-c), Mo 3d and S 2p of MoS2 and MoS2@MOx (d-e), Mn 2p of M-Mn (f), Fe 2p of M-Fe (g), Co 2p of M-Co (h), Ni 2p of M-Ni (i).
要点三:MoS2@MOx的储锂性能大幅提高
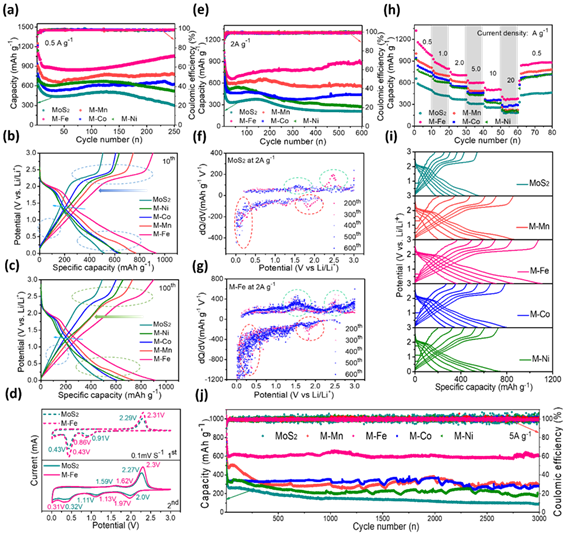
图3 纯MoS2和MoS2@MOx 复合材料的电化学性能
Figure. 3 The lithium-ions storage capabilities of the as-obtained samples: a) cycling stability at 0.5 A g−1, b, c) the charge/discharge curves of 10th and 100th loops at 0.5 A g−1, d) CV curves of MoS2 and M-Fe of 1st and 2nd loops at 0.1mV s-1, e) the long-term cycling stability at 2.0 A g−1, f, g) differential charge vs. voltage curve (dQ/dV) of 200th, 300th, 400th, 500th, 600th loops at 2.0 A g−1, i) the charge/discharge curves at different current densities h) the rate performance at various density currents, j) high-rate properties at 5.0 A g−1.
要点四:MOx电催化作用显著加快MoS2@MOx转化反应动力学
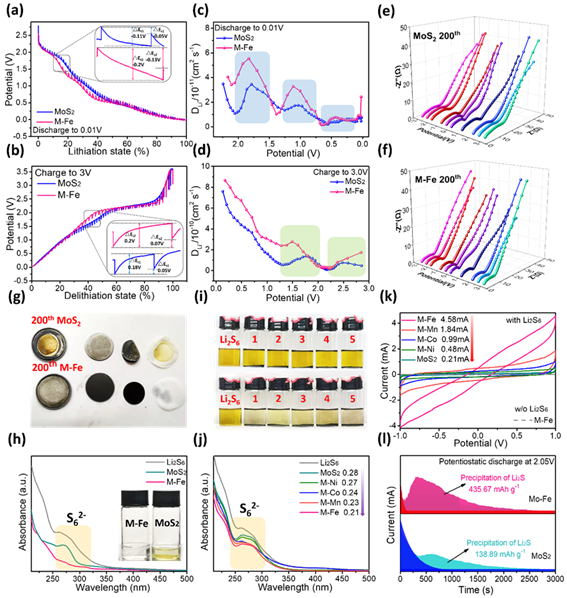
图4 纯MoS2和MoS2@Fe2O3 复合材料的转化反应动力学表征
Figure. 4 In-depth electrochemical kinetics of conversion reactions of MoS2 and M-Fe: a, b) GITT curves during the charge/discharge process, c,d) corresponding DLi+ values e, f) their fitted Nyquist plots at various potentials, g, h) optical images and UV-vis adsorption spectrums of the disassembled components from MoS2 and M-Fe half-cell after 200 loops at 2.0 A g-1, i, j) optical images and UV-vis spectrums of Li2S6 adsorption tests, k) CV curves of symmetric cells in electrolytes with/without 0.5 M Li2S6 at 50 mV s-1, l) potentiostatic discharge profiles at 2.05V with MoS2 and M-Fe electrodes.
要点五:关于Fe2O3电催化机制的理论计算
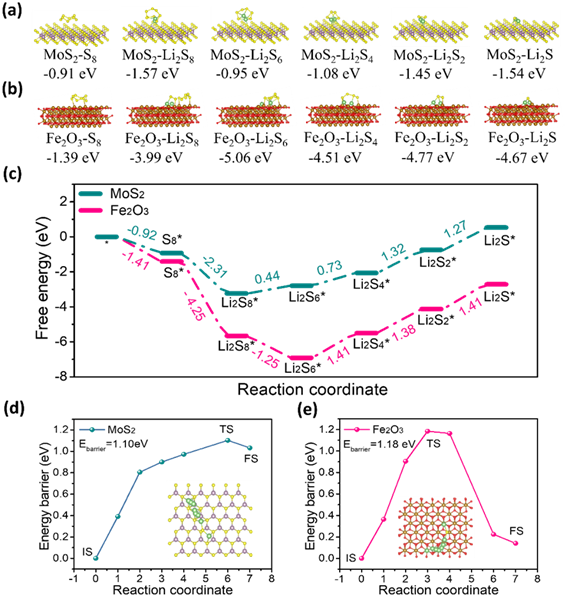
图5 纯MoS2和MoS2@Fe2O3 复合材料的DFT计算
Figure. 5 Theoretical calculations on adsorption and catalysis of LiPSs and Li2S on the surface of MoS2 and Fe2O3: the interaction configuration and corresponding binding energies of S8, Li2S8, Li2S6, Li2S4, Li2S2 and Li2S on a) MoS2, b) Fe2O3, c) energy profiles for the sulfur reduction on MoS2 and Fe2O3 substrates, decomposition barriers of Li2S and the corresponding migration pathway of Li-ion on d) MoS2, e) Fe2O3.
结 论
综上所述,本文通过化学沉淀-热处理方法合理地设计了MOx(M=Mn、Fe、Co、Ni)均匀锚定在MoS2 纳米片上的复合材料。由于过渡金属阳离子与 MoS2 的 S 原子之间的强相互作用,MoS2 和 MOx 的界面通过 Mo-S-M 化学键相互连接,为离子、电子的快速转移提供了便利的通道。
引入的 MOx 作为电催化剂可以捕获可溶性 LiPS, 并通过强 S 结合和 Li 结合加速其转化动力学。对于具有二价阳离子的 MnO、CoO 和 NiO,其3d 空轨道数随着价电子数的增加而减少,导致与 LiPS 的 S 结合减弱。与 MnO 相比,具有三价阳离子的 Fe2O3 具有相同的3d 空轨道数,Fe3+ 较小的离子半径使其与 LiPSs 的相互作用最强。
得益于界面桥键和催化功能的协同作用,MoS2@MOx的储锂能力得到显着提高。在MoS2@MOx 负极中,锂离子在嵌锂/脱锂过程中的扩散速度加快,从根本上促进了从 LiPSs 到不溶性 Li2S 的转化反应。
此外,理论计算表明,Fe2O3 可以作为双功能催化剂,在放电和充电过程中加速 LiPSs 还原和 Li2S 氧化的电化学动力学。这种简便且高效的调控方法为通过引入电催化剂制备先进储能材料提供了思路。
文 章 链 接
Engineering Metal-Sulfides with Cations-Tunable Metal-Oxides Electrocatalysts with Promoted Catalytic Conversion for Robust Ions-storage Capability
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405829721005353
通 讯 作 者 简 介

孙伟 中南大学教授 博士生导师
资源加工与生物工程学院院长。长江学者特聘教授,教育部新世纪优秀人才,湖南省121新世纪人才,湖南省531工程人才。中国矿物加工理事会秘书长,湖南省稀有金属冶金及材料制备重点实验室副主任、中国有色金属学会理事、江西省钨产业、稀土产业技术创新战略联盟副理事长,中国化学学会会员。

葛鹏 博士 副教授 硕士生导师
https://hyh.csu.edu.cn/list_textpic.jsp?urltype=tree.TreeTempUrl&wbtreeid=1019
免责声明:文章来源科学材料站;本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本公众号观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本公众号转载使用,须保留本公众号注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;版权属于原作者.









 您已经拒绝加入团体
您已经拒绝加入团体

 2022-03-18
2022-03-18
 3080
3080
 0
0